
From safeguarding personal data to protecting critical infrastructure, compliance regulations are continually reshaped by the evolving technology and societal landscapes. The CISO position has undergone a similar evolution. The transformation of the CISO role is pushing these professionals towards a more autonomous stance, approaching their work from a mindset similar to that of the external auditors and other bodies responsible for cybersecurity compliance checks.
This shift stems from boards, investors, and external parties wanting more transparency in cybersecurity programs. In fact, recent research shows that governance, risk, and compliance are now the top priorities for CISOs, and this sentiment is unlikely to change any time soon.
Cybersecurity Compliance Regulations Every CISO Should Know
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR regulates how the personal data of individuals within the EU and EEA is collected, stored, and processed.
Compliance tips for meeting GDPR requirements:
- Train client-facing teams to handle queries about data protection and privacy effectively.
- Use data minimization to only process the minimum level of personal data needed to deliver your services.
- Opt for data mapping and classification technologies to automate compliance and ensure real-time oversight of data flows and storage.
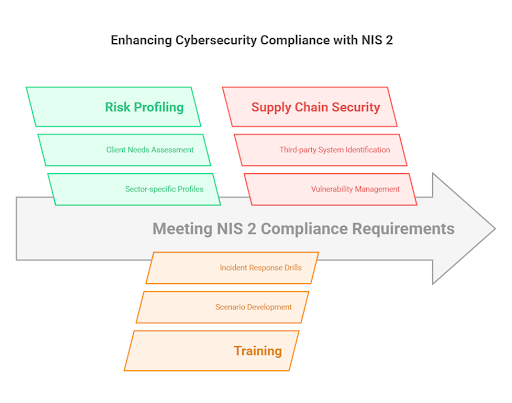
Network and Information Systems (NIS 2) Directive
Another brainchild of EU regulators, NIS 2 tries to improve cybersecurity across vital sectors such as energy, transport, health, and digital infrastructure.
Compliance tips for meeting NIS 2 requirements:
- Build tailored risk profiles for clients in each sector covered under NIS 2 (e.g., energy, transport, healthcare).
- Conduct scenario-based training sessions to prepare for rapid incident response as stipulated by the NIS 2 directive.
- Identify and secure critical third-party systems in client supply chains (NIS 2 extends accountability to supply chain vulnerabilities).
Cyber Resilience Act (CRA)
Proposed by the European Commission, the CRA came into force in December 2024, but its obligations will not apply to businesses until December 2027. It aims to set standards for the cybersecurity of any products with digital elements (e.g., connected IoT devices, firmware embedded in hardware). Products currently in development or planned for release after December 2027 need to be designed with CRA compliance in mind from the start.
Compliance tips for meeting CRA requirements:
- Map your digital product ecosystem by compiling an inventory of all products with digital elements your organization develops, distributes, or supports, including embedded software and third-party components.
- Audit and update contracts with third-party suppliers and vendors to ensure their components meet CRA standards.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Enacted in 1996 in the United States, HIPAA addresses the need to secure protected health information (PHI) by promoting data privacy and security provisions for this data. It is a critical law for businesses providing services to healthcare sector clients in the U.S.
Compliance tips for meeting HIPAA requirements:
- Design and enforce RBAC policies that limit access to PHI strictly based on the principle of least privilege.
- Use logging systems that create tamper-proof audit trails for all access to PHI.
| Regulation | Scope | Key Requirements | Compliance Tips |
| GDPR | Personal data of individuals in the EU and EEA | Lawful data collection, storage, and processing; Data subject rights (access, rectification, erasure, etc.); Data breach notification | – Train client-facing teams on data protection – Minimize data collection Use data mapping and classification tools |
| NIS 2 | Cybersecurity of vital sectors in the EU (energy, transport, health, digital infrastructure) | Risk management; Incident response; Supply chain security | – Build sector-specific risk profiles – Conduct scenario-based incident response training – Secure third-party systems in client supply chains |
| CRA | Cybersecurity of products with digital elements (IoT devices, firmware) | Security standards for product development and lifecycle; Vulnerability management and reporting | – Map digital product ecosystem – Audit and update supplier contracts to ensure CRA compliance |
| HIPAA | Protected health information (PHI) in the United States | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI; Access control; Audit trails | – Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) for PHI – Use tamper-proof logging systems for PHI access |
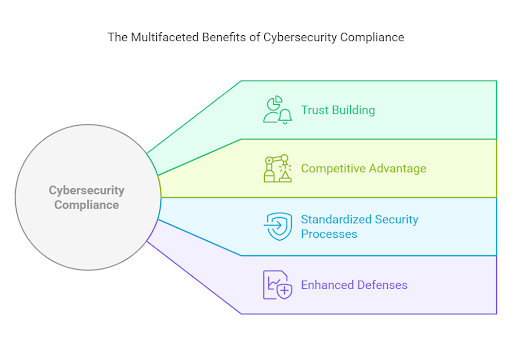
Reasons Why You Should Prioritize Cybersecurity Compliance
It might seem that the sole driver of cybersecurity compliance is avoiding harsh penalties (more on those later), but a CISO’s role is to shift perspective and view compliance as something more beneficial than just bypassing financial fallouts.
In a world where data breaches often make news headlines, trust is as valuable as the services you provide. Businesses prioritizing compliance gain a clear competitive edge in winning and retaining clients, especially those in heavily regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and energy.
Compliance standardizes security processes as regulations are built around industry best practices for cybersecurity. Adhering to them inherently improves your defenses, and requirements like vulnerability assessments, incident response plans, and data encryption align closely with proactive risk management.
Penalties and Consequences for Cybersecurity Compliance Failures
Penalties for cybersecurity compliance failures vary greatly depending on the specific regulation and the nature of the violation. To illustrate the potential consequences, let’s take a look at two prominent examples: GDPR and HIPAA.
GDPR enforces a tiered approach to fines:
- Lower Tier: Fines up to €10 million or 2% of the company’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher, for less severe infringements.
- Upper Tier: Fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher, for more serious violations.
HIPAA violations can result in:
Civil penalties with fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million for identical provisions.
Beyond these clearly defined penalties, there are other costs of compliance failures that make for hefty financial fallouts. Non-compliance can:
- Lead to higher cyber insurance premiums.
- Severely damage a company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and potential business downturns.
- Trigger regulatory investigations and corrective actions that disrupt business operations and divert resources from strategic initiatives.
- Result in legal proceedings, including class-action lawsuits, especially in jurisdictions that allow private rights of action for data breaches.
8 Steps to Set Up the Ultimate Cybersecurity Compliance Program
Creating a robust and proactive compliance program isn’t about checking boxes; it’s about facilitating a culture of security and resilience. Here’s an eight-step guide CISOs can use to establish a comprehensive cybersecurity compliance program that effectively mitigates risks.
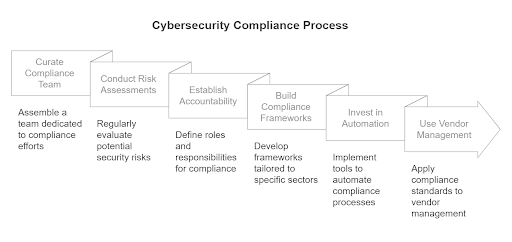
1. Curate a Dedicated Compliance Team
While compliance ultimately falls on the CISO’s desk, the responsibility and to-do lists are far too comprehensive for one person. A focused compliance team ensures there’s always someone driving the agenda, staying ahead of regulations, and holding the organization accountable. Build a team with cross-functional expertise—security, legal, IT, and operations.
This group should lead audits, track regulatory updates, and manage client-facing compliance services.
2. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Tools like Cynomi can save days of manual effort by tailoring assessments to specific regulations, automatically identifying gaps, and prioritizing fixes. Make this process iterative so you’re constantly adapting to new threats and system changes.
3. Establish Clear Accountability
Compliance tasks often fall through the cracks because roles are not clearly defined. Accountability ensures the right people are handling the right aspects of compliance.
You can use a RACI matrix to map out responsibilities for everyone involved—who owns the risk assessments, who signs off on policies, and who manages incident reporting. Share this framework across teams so there’s zero ambiguity when auditors or clients ask tough questions.
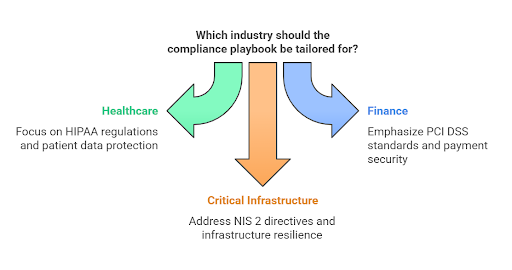
4. Build Sector-specific Compliance Frameworks
Your clients don’t all play by the same rules, and neither should your compliance strategy. An effective strategy is to develop tailored playbooks for industries like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI DSS), or critical infrastructure (NIS 2).
Include specific risk scenarios, required controls, and reporting templates. These playbooks aren’t just useful for audits—they also show clients you understand their world.
5. Invest in Compliance Automation
CISOs don’t need convincing about the benefits of automation, but many need the justification to include it in the next budget. Invest in tools that can track compliance continuously, generate audit-ready reports, and identify vulnerabilities in real time.
Integrate these systems into your cybersecurity workflows to reduce redundancy and improve visibility across your organization and client environments.
6. Use a Compliance-driven Vendor Management Program
Regulations like GDPR and NIS 2 hold CISOs accountable for the actions of suppliers and partners. A best practice requires vendors to provide evidence of their compliance posture, such as certifications or audit reports. Here’s where automated vendor risk management tools can help streamline the execution of regular security control assessments and flag non-compliance in contracts.
7. Centralize Documentation
One of CISOs’ biggest pain points during audits is the inability to quickly produce compliance documentation. To address this, use a centralized repository to store all compliance-related documents, policies, and reports. Implement access controls to ensure sensitive information is only available to authorized users.
Automate document versioning and updates to maintain accuracy and alignment with evolving regulations.
8. Run Real-world Compliance Scenarios
Simulations aren’t just for incident response—they can also test your employees’ compliance readiness under real-world conditions.
Create mock scenarios replicating common compliance challenges, such as a ransomware attack requiring GDPR’s 72-hour breach notification. Evaluate how well your team handles reporting, documentation, and communication with regulators.
Complete Visibility and Compliance Automation With Cynomi
One factor that rings true when discussing compliance is the need to automate. Choosing a vCISO platform like Cynomi significantly reduces the manual work MSPs/MSSPs must undertake to support clients with frameworks like GDPR and NIS 2, as discussed above.
Cynomi combines CISO expertise with AI to automate vCISO tasks, enabling MSPs/MSSPs to focus less on repetitive compliance assessments and more on upselling services and delivering true value to clients. Organizations like CA2 Security have already used Cynomi’s vCISO to upgrade to pre-built and streamlined risk assessments, enabling them to understand their clients’ domains and security gaps.
For example, Cynomi tailors questionnaires and scans for each client to automatically build each client’s cyber profile. Then, the Cynomi engine continually parses the cyber profile of each client against relevant external sources like frameworks and industry benchmarks. MSPs/MSSPs can gain total visibility over compliance efforts and gaps by leveraging Cynomi’s findings to substantiate service upsells and demonstrate the impact of services. Request your demo today.