Cybercrime is the ultimate headline-grabbing topic, garnering attention and gossip from the tech industry, journalists, and the general public alike. Getting mentioned in the small print is a disaster for any brand’s carefully crafted reputation, not to mention the financial and legal consequences that loom overhead.
According to some estimates, the global cost of cybercrime will inflate to a dizzying $23.84 trillion by 2027. As a result, the cybersecurity market will grow to a value of around $533.9 billion by 2032, up from $193 billion in 2023. There’s big money in being a cyber villain and even more cash to make as a superhero savior.
For managed security service providers (MSSPs), this means ample opportunities to provide clients with the services they need to protect digital assets, business continuity, and market reputation, plus comply with regulatory requirements for data protection and cybersecurity control implementations. One service frequently found in the portfolios of leading MSSPs is quantitative cyber risk assessments, a strategy that helps inform and enhance clients’ cybersecurity posture.
What is a quantitative risk assessment?
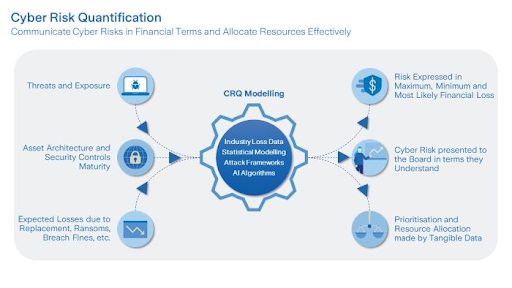
A quantitative risk assessment (QRA) in cybersecurity, also known as cyber risk quantification (CRQ) is the process of assigning numerical values to the financial impact of cyber events on an organization.
Quantitative risk assessments use numerical data that can be measured and calculated to supply actionable insights. The insights generated by the quantitative risk assessment method in cybersecurity are typically expressed in monetary terms (like annual rate of occurrence and annual loss expectancy). The goal is to direct the focus of cybersecurity efforts and the distribution of budgets to address the most critical issues and vulnerabilities that put the business at risk, aiming to be repeatable and provide clear insights to all relevant stakeholders.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Risk Assessment in Cybersecurity
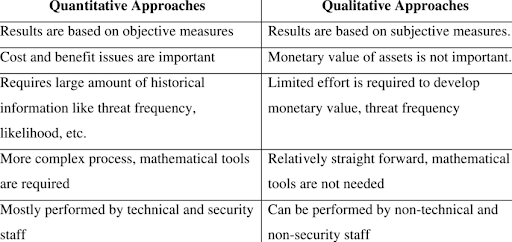
Quantitative and qualitative approaches to cyber risk assessment are the two main methodologies employed in cyber risk analysis. While quantitative risk assessments rely on measurable and concrete data, qualitative risk assessments depend on the expertise and judgment of the stakeholders involved in the risk assessment process.
Whereas the insights generated by quantitative risk assessments are typically expressed in monetary terms, risk impact in qualitative cyber risk analysis is frequently categorized as low, medium, or high, with the risk of occurrence expressed in percentages. In addition, while qualitative risk assessments are usually easier and much quicker to execute, they can be influenced by biases and are less objective than quantitative cyber risk assessments.
When it comes to conducting a comprehensive cyber risk assessment, combining both quantitative and qualitative risk assessment methods is key to gaining a holistic understanding of the specific cyber risk factors every organization must address.
With quantitative analysis, you can uncover more potentially invisible threats that qualitative analysis can help contextualize for a broader view and deeper understanding of each potential risk to the systems of a specific organization. This approach is critical in making informed decisions and effectively managing cyber risk.
How to Perform a Quantitative Risk Assessment in Cybersecurity
1. Prepare Your Data
A quantitative risk assessment in cybersecurity requires, first and foremost, a significant amount of internal and external data sources. These include cyber intelligence feeds, SOC logs, root cause analysis documents, control effectiveness reports, and other governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) inputs, to name a few. All this information must be standardized and normalized to ensure accuracy and consistency before you can begin the step-by-step process of cyber risk quantification.
2. Identify Critical Assets
Before you can quantify risk, you must understand what you need to protect in the first place. Begin by comprehensively identifying and categorizing your client’s critical assets, including risk assessment software, hardware, data records (physical and digital), reputational variables, and even employees whose absence or compromise may negatively impact business operations.
3. Assign Asset Values
Not all assets need the same level of protection and cybersecurity investment. Once you have all business assets cataloged, you will need to determine how much impact a compromise of each asset may have on the business. Factors to consider in asset valuation include access to sensitive data or controls and their role in supporting smooth business operations.
4. Conduct a Vulnerability Study
Next, you must identify the risk factors for each high-value asset you’ve identified and evaluated. This step entails conducting a vulnerability study that explores the required threat detection strategies, inherent vulnerabilities, data sensitivity, configuration drift gaps, and other risks relevant to the specific clients for which you are conducting the quantitative risk assessment.
The vulnerability study also entails analyzing the severity and exploitability of vulnerabilities that may put high-value assets at risk. The data in a vulnerability study typically comes from vulnerability scanners (some platforms, such as Cynomi’s vCISO, have vulnerability scanners built-in), incident response reports, threat intelligence feeds, and more.
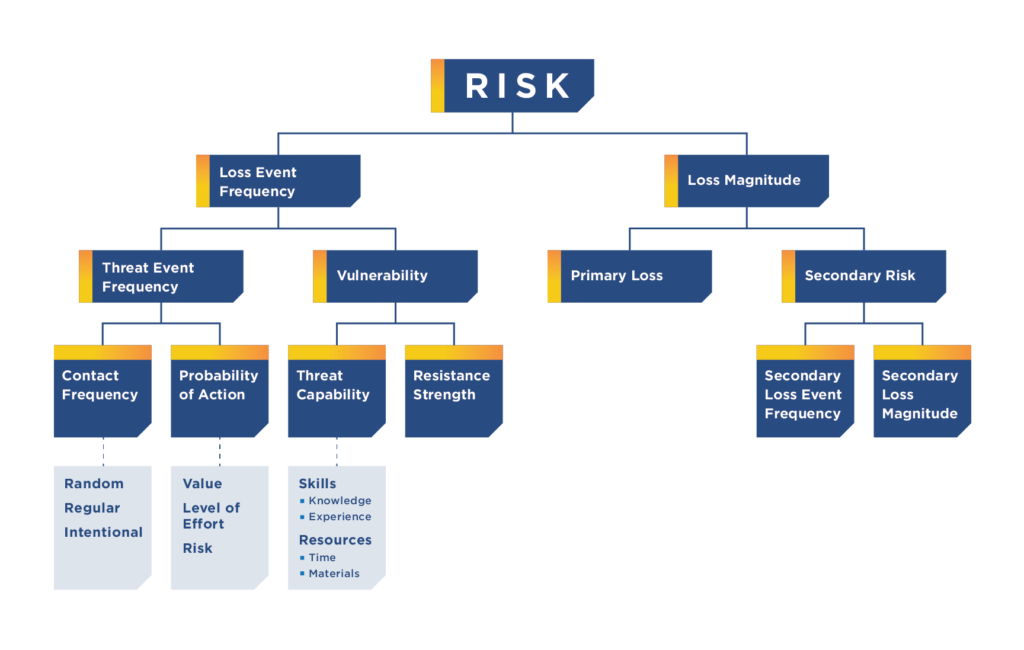
5. Estimate the Frequency and Loss Expectancy for Each Risk Factor
Now, it’s the challenging part of quantifying both the impact and likelihood of threat scenarios. Depending on your modeling framework of choice, this may entail estimating the Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) and the Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE) for each risk factor using historical data, expert opinions, and industry benchmarks. These key variables make it much easier to prioritize high-impact scenarios with high likelihood while putting a “price tag” on each.
6. Aggregate and Communicate Your Findings
Numbers don’t mean much if you don’t communicate them to client stakeholders in a way that promotes action. With the risk scores you’ve calculated, you can begin to outline the client’s overall risk posture. Since all the values are expressed in monetary terms, communicating them to management and decision-makers should be a lot easier, and enable educated engineering capital appropriation.
Be sure to present the findings using visual aids like charts, graphs, heat maps, risk distribution charts, and any other method or format you think is best to help stakeholders (including non-technical ones) fully comprehend the risk landscape in relation to security frameworks like NIST.
7. Monitor and Update
Cyber threats change, and clients grow, adopting new technologies and making new hires. Therefore, last year’s cyber risk quantification methods and resources may no longer be relevant. In some organizations, change can be even more rapid, with regular updates needed to the cyber risk quantification processes and data sources on a constant and continuous basis.
That said, updating the quantitive risk assessment in cybersecurity is much easier than the initial painstakingly long and complex task of gathering and standardizing data and aligning client risk strategies with cybersecurity efforts.
Streamlining Quantitative Risk Assessment at Scale with Cynomi
Comprehensive and effective quantitative risk assessment in cybersecurity is no easy feat. It requires huge resource investments and a team of skilled professionals, and it frequently consumes a great deal of time and resources from everyone involved.
However, MSP/MSSPs can streamline and automate cyber risk quantification using your existing resources and headcount with Cynomi. Cynomi is a vCISO platform combining proprietary AI algorithms with CISO-level knowledge to dramatically reduce the manual work in conducting regular quantitative risk assessments for multiple clients.
With Cynomi, MSPs/MSSPs can shorten the completion time of quantitative risk assessments from weeks to hours with built-in self-guided discovery questionnaires that help you gain visibility into your clients’ cybersecurity posture. By automatically delivering scans and questionnaires according to the cyber profile of each client, Cynomi streamlines quantitative risk assessment processes to uncover critical vulnerabilities without extensive manual data entry and analysis.
Request a demo to see why Cynomi is a world-leading choice for comprehensive qualitative risk assessments.