
Can your clients afford the cost of a cyber attack? Can you? The rising frequency and sophistication of cyber threats mean businesses face unprecedented risk. Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) are constantly battling the concept that complete risk elimination is impossible – strategic and comprehensive prevention is the key.
Cyber threats have surged dramatically, with a 72% increase in data breaches last year compared to two years prior. Such incidents can have severe consequences for your MSP and clients, including financial losses, legal liabilities, and tarnished reputations. Fraud risk matrix assessment tables are a vital asset for MSPs/MSSPs in such a volatile landscape, turning threats into clear priorities and helping you create effective strategies to keep your clients a step ahead of cyber attacks.
What is a risk assessment table?
A risk assessment table, often known as a risk matrix, is a powerful tool that helps organizations systematically evaluate and manage potential risks. It visually represents potential risks in a structured grid based on their likelihood of occurrence and impact on the organization.
This matrix format makes it easier to identify which risks require immediate concern and which can be monitored over time. Such a tool is essential where managing risk is not just a best practice but a necessity – which is nowadays true for almost any organization.
Let’s look at a few high-risk industries.For example, a finance risk matrix helps identify data security and transaction integrity threats. In healthcare, it helps manage risks related to patient data and compliance with stringent regulatory standards like HIPAA. These sectors can effectively pinpoint vulnerabilities using a risk assessment table, helping them ensure regulatory compliance and identify targeted risk mitigation strategies.
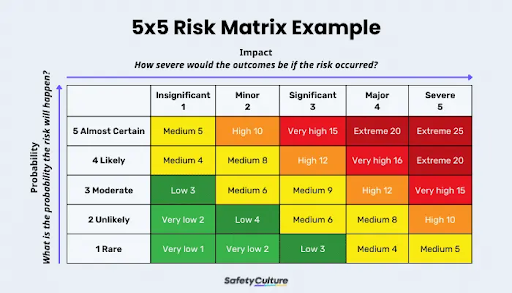
How to Use a Risk Assessment Table
A popular choice for risk assessment is the 5×5 matrix, which uses a five-point scale. One axis represents how likely a risk is to happen, and the other indicates the potential severity of its impact. This scale provides a detailed, granular view of risks, making it easier to prioritize them.
The specific type of risk assessment table you use doesn’t ultimately matter – what’s important is how effectively you use it to evaluate and manage risks. The prioritization process remains largely the same.
You should regularly include risk assessment tables in the risk management routine for your clients’ best results. Plus, you can update the table with new risks and revise existing ones as situations change. The table should serve as a living document to identify the most pressing risks and allocate resources effectively to prevent disruptions and protect critical functions.
Why should you use a risk assessment table?
As risk assessment table provides MSPs/MSSPs with a crucial edge in cybersecurity management. It is a type of risk assessment template that delivers several key advantages, enhancing your ability to safeguard clients’ systems and data.
Improved Risk Visibility
Without risk visibility, your clients can be in the dark, unable to identify their most vulnerable areas. A risk matrix offers a clear, visual overview of potential threats, helping you quickly identify specific risks such as unauthorized access or data breaches. This visibility allows you to offer and implement security measures appropriate for each client’s unique vulnerabilities.
Prioritized Risk Management
Without prioritization, your clients risk spreading their resources too thin, attempting to address every potential threat simultaneously. This approach can lead to a scattergun technique where critical issues are neglected or underfunded, resulting in major vulnerabilities being overlooked. A risk assessment table helps you zero in on the most critical threats. Instead of treating all risks equally, it allows you to advise clients in prioritizing and addressing the most pressing issues first.
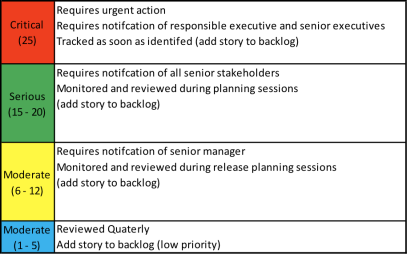
Enhanced Decision-Making
A comprehensive overview of all identified risks allows decision-makers in MSPs/MSSPs and your clients’ organizations to allocate resources more effectively. You can make informed decisions about where to focus efforts and budget, such as investing in advanced threat detection tools for high-risk areas or strengthening security protocols for vulnerable systems. It is particularly helpful if your risk management strategies are collated in one place, such as in a vCISO platform.
Proactive Client Engagement
Using a structured approach to risk management with a risk assessment table can help you engage proactively with clients. Clearly outlining risks and detailing the actions being taken to mitigate them helps build trust in MSPs/MSSPs. This strategy promotes a more collaborative relationship, where clients feel involved and informed about the measures protecting their data and systems. This relationship of trust is a foundation for upselling and cross-selling opportunities.
6 Steps to Create a Risk Assessment Table
Building a risk assessment table equips you with the tools to systematically identify, evaluate, and prioritize client risks. Here’s a practical, step-by-step guide to help you create one.
1. Identify Sources of Risk
Begin by identifying risks specific to your client’s industry and operations. These could include cyber threats, operational failures, or external events.
Internal risks
- Operational: System failures, data loss, human error
- Financial: Budget constraints, project overruns
- Compliance: Regulatory violations, legal issues
- Reputational: Negative publicity, brand damage
External risks
- Cybersecurity: Phishing, ransomware, data breaches
- Natural Disasters: Floods, earthquakes, fires
- Economic Downturn: Market fluctuations, supply chain disruptions
For instance, risks in a financial services firm might include phishing attacks targeting customer data or insider threats where employees misuse sensitive information. Conduct regular company-specific risk identification workshops with stakeholders to ensure a comprehensive and updated list of potential risks.
2. Define Risk Criteria
Set clear criteria to measure how likely each risk is and how serious its impact could be. Consider customizing these scales to align with your client’s risk tolerance and industry standards. For example, with a five-point risk assessment table, you might use:
Likelihood
- Rare: Once every ten years or more
- Unlikely: Once every five years
- Possible: Could happen annually
- Likely: Several times a year
- Almost Certain: Frequent occurrences
Impact
- Insignificant: Minimal disruption, easily recoverable
- Minor: Limited impact, manageable consequences
- Moderate: Noticeable impact, requires action
- Major: Significant disruption, substantial losses
- Catastrophic: Severe financial or reputational damage, potential for business failure
3. Gather Data
Collect relevant current and historical data to support the risk assessment table.
Historical data
- Incident Logs: Review past security incidents, system failures, and near misses.
- Audit Reports: Examine findings from internal and external audits.
- Insurance Claims: Analyze data on past claims and losses.
Current data
- Threat Intelligence: Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Industry Reports: Benchmark against industry-specific risk assessments.
- Vendor Assessments: Evaluate the security posture of third-party vendors.
Review logs and records of past security breaches, system failures, and other incidents. Extract data from your client’s firewall logs, intrusion detection systems, and incident response reports over the last five years to identify recurring patterns and high-risk areas.
4. Evaluate Risks
Assess the likelihood and impact of each risk using the predefined criteria and historical data. For likelihood, determine how often the risk has occurred or might occur. For example, if a tech firm has experienced multiple DDoS attacks in the past two years, the likelihood of this might be marked as ‘Almost Certain.’ You can consider:
- Frequency: How often has this risk occurred in the past? How likely is it to happen again?
- Severity: What are the potential consequences of this risk? How would it affect your client’s operations, finances, reputation, and compliance?
- Vulnerabilities: Are there any weaknesses in your client’s systems or processes that could be exploited?
- Mitigation Measures: Are there existing controls in place to reduce the likelihood or impact of this risk? How effective are they?
5. Plot on Matrix
A risk matrix is a visual tool for prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and impact. Create a table with likelihood on one axis and impact on the other. Each cell in the matrix represents a different level of risk.
Place each risk in the appropriate cell of the matrix based on its likelihood and impact scores. Use color coding or numerical values to indicate the level of risk (e.g., red for high risk, yellow for medium risk, green for low risk).
6. Prioritize Remediation Efforts
Focus your resources on the risks that fall into the high-likelihood, high-impact quadrant of the matrix. These risks pose the greatest threat to your client and require immediate attention. Develop and implement mitigation plans for each high-risk item, including:
- Risk Reduction: Implement security controls, backup procedures, or redundancies to minimize the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Risk Transfer: Consider cyber insurance coverage checklist for your clients and your MSP/MSSP.
- Risk Acceptance: For low-impact risks, it may be acceptable to simply implement continuous security monitoring tools and have a contingency plan in place.
Regularly review and update your risk assessment table to ensure it remains relevant and effective in protecting your client’s assets and reputation. Remember, risk management is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, adaptability, and dynamic risk assessment strategies.

Let Cynomi Handle the Heavy Lifting
Managing cybersecurity risks requires more than just the right tools – it’s about strategically anticipating and countering potential threats. Risk assessment tables break down complex threats into clear priorities, making it easier to allocate resources where they are needed most. They are essential to a proactive cybersecurity strategy, empowering MSPs and MSSPs to protect clients’ valuable assets.
With Cynomi, you can provide clients with comprehensive risk assessments without manual completion – no more tables, complex spreadsheets, or calculations. Cynomi automates the manual, time-consuming work of risk assessments, speeding up the process from days to hours. It tailors the relevant questionnaires and scans to automatically build each client’s cyber profile, using guided questionnaires and express scans to uncover critical vulnerabilities.