
For many SMBs, managing cyber risk is a high-stakes challenge without the resources to match. Without in-house security expertise, they rely on you—MSPs and MSSPs—to bring clarity to their risk landscape and deliver meaningful IT assessments.
The stakes are high, and the urgency is real. Data breaches soared in 2023, climbing 72% over the record-breaking levels of 2021. IT risk assessments are a big win for your clients, meaning a clearer view of their security gaps, stronger defences, and a solid handle on compliance.
For MSPs/MSSPs, this strategy builds trust, strengthens relationships, and opens the door to more opportunities. Yet, delivering these assessments isn’t always easy—they require time, specialized expertise, and resources that can stretch your team thin.
What’s the purpose of an IT risk assessment?
An IT risk assessment is about pinpointing the specific risks that could hit a client the hardest. For MSPs and MSSPs, an IT risk assessment helps you go beyond generic security advice and deliver targeted, high-value solutions that your clients actually need. This strategy helps prioritize what matters, showing exactly where the client’s security gaps are, how big the potential impacts could be, and where to focus resources for the greatest protection.
IT Risk Assessment Methodologies
MSPs typically use two main methods in IT risk assessments, depending on the data available and the client’s priorities:
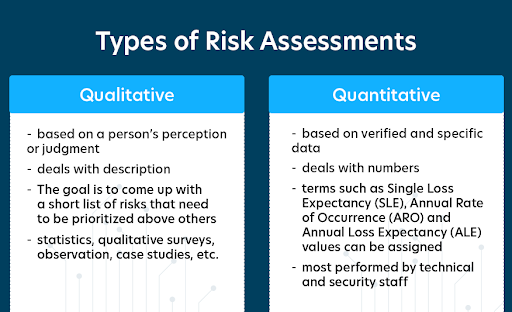
- Quantitative: Puts a dollar amount on risks, which is perfect for clients who want a clear financial picture. This method uses metrics like Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE) to rank risks by financial impact, making it easier to decide where to allocate resources.
- Qualitative: Uses expert judgment for risks that don’t have exact numbers, like reputation damage or regulatory issues. Risks are rated as “high,” “medium,” or “low” based on their likelihood and impact.
Why Your MSP/MSSP Clients Need IT Risk Assessments
With an IT risk assessment, MSPs can go beyond one-size-fits-all security. It’s about finding the gaps that could hurt the client most, whether that’s weak access controls or unpatched software. By targeting these specific issues, you can offer security solutions that fit like a glove, showing clients exactly what they’re getting and why it matters.
A well-executed IT risk assessment also enables clients to sidestep expensive disasters before they happen. Spotting a vulnerability in, say, a client’s firewall can mean the difference between business as usual and a ransomware attack that could cost thousands. Clients get peace of mind knowing their provider has a handle on their risks, and you can build your reputation as a proactive, essential MSP/MSSP partner.
Compliance is a constant pressure for clients in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and critical national infrastructure (CNI). IT risk assessments flag compliance issues early, allowing your clients to fix problems before auditors get involved and positioning you as an invaluable resource for keeping them compliant year-round.
What You Should Do Before Conducting an IT Risk Assessment
Before an IT risk assessment kicks off, MSPs/MSSPs should guide clients through a few essential prep steps.
- Start by securing stakeholder buy-in to build support and resources for any actions needed afterward.
- Communicate the plan across teams so everyone understands the goals and their role—this avoids confusion and makes data gathering more seamless.
- Finally, help clients choose the right assessment methodology: quantitative for financial impact or qualitative for non-monetary risks.
10 Essential Components of Every Good IT Risk Assessment
1. Define the Scope and Context
Begin by setting precise boundaries for the IT risk assessment. Is the focus on protecting client data in the cloud, securing internal networks, or both? For example, if the client primarily handles sensitive customer data, the scope might prioritize database security and cloud configurations.
2. Identify Key Assets
List out critical assets that, if compromised, could disrupt operations or lead to severe losses. For a financial services client, this might include transaction databases, customer account details, or payment processing systems. By identifying these key assets upfront in the IT risk assessment, MSPs/MSSPs can narrow the focus to what matters most, avoiding time spent on low-impact areas.

3. Conduct a Threat Assessment
This step involves identifying any and all potential threats that could impact the assets in scope. Consider various threat sources, from cybercriminals to insider threats, as well as natural disasters or even vendor risks. MSPs/MSSPs can provide clients with a comprehensive risk profile by understanding what could go wrong and how likely each threat is.
It’s critical to extend the threat assessment to third parties too, considering vendor risk in the bigger picture. After all, a breach, vulnerability, or risk at any point in the supply chain can trickle down to clients, even if their business isn’t directly affected.
4. Use Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Vulnerability scans offer a quick but detailed look at weak points across a client’s network and systems. MSPs/MSSPs can leverage automated scanning tools to speed up the process of identifying gaps, like outdated software or misconfigured security settings, that could serve as entry points for attackers.
5. Assess Business Impact
Risk is about more than just the threat itself. It’s also about the potential fallout and business impact. Quantify the potential impact of each identified risk on the client’s business operations. For example, a breach in a client’s email system might lead to phishing attacks, impacting both internal security and client trust. By tying risks to specific operational impacts, MSPs can help clients see the real-world consequences of their vulnerabilities.
6. Prioritize and Evaluate Risks
Use a structured ranking system in the IT risk assessment to prioritize risks based on likelihood (the chance of occurrence) and impact (potential damage):
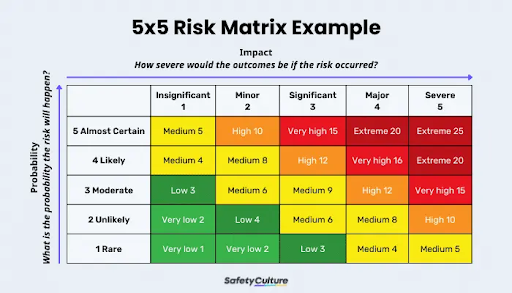
- Risk Matrix: Create a grid with likelihood on one axis and impact on the other that categorizes risks as Low, Medium, High, or Critical.
- Risk Scoring: Assign numerical scores to each risk component. Multiply the scores to get an overall risk score. This strategy quantifies risks so clients can rank them in descending order, focusing first on the highest scores.
7. Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies
For each high-priority risk, MSPs/MSSPs should create targeted strategies to reduce the likelihood or lessen the impact on clients. Start by pinpointing the root cause, then outline specific actions like setting up firewalls, tightening access controls, or enforcing multi-factor authentication.
For risks that can’t be entirely prevented, develop contingency plans, such as regular data backups, to minimize potential damage. Assign roles and timelines within the client’s team, tracking and adjusting these strategies as needed to keep them effective.
8. Establish an Ongoing Monitoring Strategy
A one-time IT risk assessment is a snapshot, but risks evolve. For clients in fast-paced industries or with frequently changing systems, you can set up automated alerts to monitor network traffic, detect unusual activity, and flag unpatched vulnerabilities. Regular vulnerability scans, real-time threat detection, and scheduled security audits help MSPs/MSSPs spot and address new emerging risks for clients.
9. Document the Risk Assessment Process
Accurate documentation captures the findings, analysis, and decisions made during the risk assessment. This record is valuable for accountability, regulatory compliance, and future assessments. It gives the client a reference point for reviewing previous vulnerabilities and understanding the evolution of their security posture over time.
10. Educate Stakeholders and Team Members
Once the assessment is complete, it’s time to communicate the findings to key client stakeholders and IT teams through engaging reports. Use clear, non-technical language to explain each risk for non-technical stakeholders, its impact, and the actions needed to mitigate it. Visual aids like risk matrices and priority lists can highlight urgent items, while step-by-step guides offer clients a clear roadmap.
MSPs/MSSPs can also choose cyber risk assessment tools and platforms, like Cynomi’s vCISO Platform, that provide a customizable operations dashboard and one-click reporting. These platforms give you everything you need to show automated reports to clients, empowering them to take ownership of their security measures.
How Cynomi Simplifies the IT Risk Assessment Process
Conducting detailed risk assessments for each client can quickly become time-intensive and resource-demanding. With built-in automated smart and adaptive questionnaires, Cynomi makes the risk assessment process 40-60% quicker and much simpler.
Even those without formal risk assessment training can leverage Cynomi’s intuitive, step-by-step guidance and embedded knowledge base to conduct thorough assessments. Cynomi’s automated scans identify vulnerabilities in public-facing resources, and the benchmarking tool provides a clear, actionable risk score by measuring clients’ cyber risk profiles against industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Ready to simplify IT risk assessment for your clients? Book your demo today.