The Essential Cyber Insurance Risk Assessment [XLS Download]
![The Essential cyber insurance risk assessment [XLS Download]](https://cynomi.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/The-Essential-cyber-insurance-risk-assessment-XLS-Download-1-1.png)
Behind every fast-paced phishing simulation and the adrenaline rush of incident response, there’s a less riveting and glamorous aspect of cybersecurity: insurance coverage. While insurance, in general, may not stir excitement among organizations, it’s the safety net that ensures business continuity in the worst-case scenarios.
Cybercrime will reach lucrative new heights in 2025, costing businesses $10.5 trillion. So, it’s no wonder that companies are looking for more coverage; in turn, insurers expect greater visibility into their policymakers’ cybersecurity practices. Hence, many organizations turn to third-party consultants and MSPs/MSSPs to ease the process of conducting a cyber insurance risk assessment on their side.
What is a cyber insurance risk assessment?
A cyber insurance risk assessment is a high-level audit of an organization’s risk levels for insurance underwriting. It entails a systematic evaluation of cybersecurity threats to organizations and measures taken to mitigate them, including processes, technologies, and protocols for day-to-day employee operations.
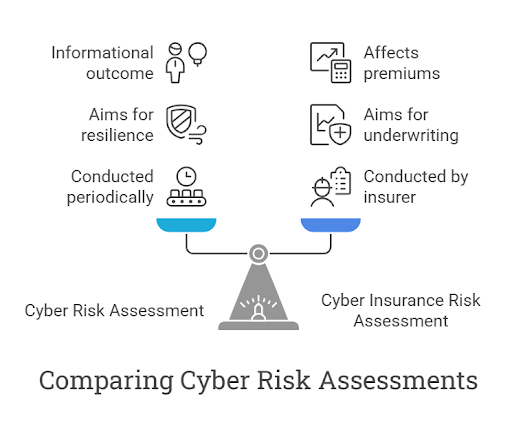
Cyber Risk Assessment vs Cyber Insurance Risk Assessment
A cyber insurance risk assessment is similar to a cyber risk assessment in many ways. Both are in-depth audits that aim to identify and prioritize potential cybersecurity risks to the organization’s IT infrastructure, processes, and digital assets. However, there are three key differences between the two:
- Who conducts the assessment: A cyber risk assessment is typically conducted periodically, either internally or through a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP), while a cyber insurance risk assessment is executed by an insurer prior to issuing a cyber insurance policy.
- The goal of the assessment: While cyber risk assessments aim to estimate the overall resilience of the organization’s IT assets and infrastructure, cyber insurance risk assessments are primarily used in the underwriting process of cyber insurance policies to determine whether and what coverage should be approved.
- The outcome: Cyber risk assessments are usually informational in nature and can guide businesses in updating and adjusting their cybersecurity strategies and protocols. Cyber insurance risk assessments, on the other hand, impact the premiums and coverage an insurer will be willing to provide based on the level of risk measured.
From an MSSP perspective, helping organizations prepare for insurers’ cyber insurance risk assessments is an added-value service with increasing demand. By providing their clients with a cyber insurance risk assessment report, MSSPs can aid businesses in pinpointing and bridging the security gaps and cyber risks that may impact the likelihood of policy approval at a cost-effective premium.
The Headache of Qualifying for Cyber Insurance
Insurers increasingly scrutinize organizations’ cybersecurity strategies during the underwriting process and provide cost-effective policies only to those who prove their commitment to active protection against cyber threats. As a result, organizations must take the time to prepare for a cyber insurance risk assessment and conduct one internally beforehand to ensure they can address the gaps and issues that may hinder cost-effective and comprehensive cyber insurance.
How a Cyber Insurance Risk Assessment Helps MSP/MSSP Clients Get Their Insurance Right
When conducted with the help of an MSP/MSSP, a cyber insurance risk assessment acts as a rehearsal for the assessment that a cyber insurance provider will conduct. It is also a vital service that aids businesses in defining and ensuring proper coverage for the specific areas where risks cannot be prevented or mitigated fully through other means.
Your customers can also benefit from a cyber insurance risk assessment as an overview of their business’s cybersecurity posture and specific risks that demand adequate attention. In a sense, it is equivalent to a cyber risk assessment regularly conducted internally.
For MSPs/MSSPs, this is an opportunity to upsell services and solutions to mitigate the risks discovered and lower the overall cyber risk to the organization. For businesses, the expertise and insights provided by a professional MSSP are invaluable in addressing risks and choosing the right policy that aligns with the specific organization’s risk profile and coverage needs.
The Essential Cyber Insurance Risk Assessment Template
Cyber insurance policy coverage and costs depend heavily on numerous factors (like industry, business size, etc). Nonetheless, below is a list of requirements for a comprehensive cyber insurance risk assessment template.
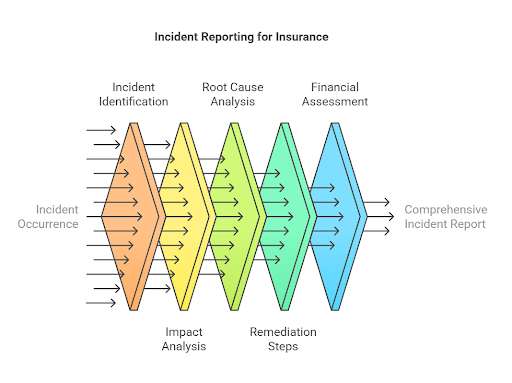
1. Organize Incident and Cyber Loss History
Like with other types of insurance, carriers will ask about past incidents and events that had a financial impact on the business before they issue a policy. In some cases, the insurer may demand that the policy applicant provide detailed reports for each event or incident, including:
- Date and time of the incident
- Type of incident (e.g., ransomware, data breach, phishing attack, DDoS attack)
- Description of the incident and its impact
- Root cause analysis
- Remediation steps taken
- Total financial losses incurred (including recovery costs, legal fees, etc.)
- Duration of downtime and business disruption
2. Leverage Compliance With Cybersecurity Frameworks
Adhering to voluntary cyber security industry standards and data privacy regulations is a proven way to lower cyber risk. It demonstrates to insurers that many controls and policies they expect to see are already in place. Some of the standards and frameworks that often appear in cyber insurance application forms include:
That said, customers should be prepared to pay a higher premium when looking for a comprehensive cyber insurance policy that covers non-compliance fines and related costs.
3. Set Formal Information Security Policies and Incident Response Plans
Another best practice is to invest in a set of cyber security policies and a comprehensive incident response plan. Depending on the type of organization, MSP/MSSP clients may require different types of policies, including but not limited to:
- Network security policy: Defines rules for network access, firewall management, and network segmentation.
- Remote access policy: Secures remote connections with measures like VPNs and multi-factor authentication.
- Password management policy: Enforces strong password creation, complexity requirements, and regular updates.
- Data management policy: Governs data handling, storage, access, and retention.
- Acceptable use policy: Defines acceptable employee behavior regarding technology and internet usage.
4. Enforce Strong Access Controls
Prevention of unauthorized access to sensitive information is vital to any cyber security strategy, and insurers expect businesses to implement robust access controls to mitigate identity-related breaches.
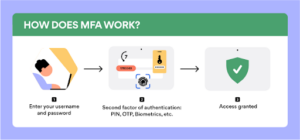
One of insurers’ most basic requirements is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to company accounts through the use of compromised passwords alone. Insurers will often expect organizations to employ identity access management (IAM), role-based access, and user monitoring to protect sensitive data.
5. Implement Robust Backup and Recovery Strategies
Strong data backup and recovery policies can make a huge difference in the cost of a cyber attack. Insurers will often demand that you store off-site or offline backups of mission-critical data and have a disaster recovery plan that details the process of service restoration and data recovery.
In addition to backups and rollback procedures for impacted systems, it’s important to adopt a testing policy for backups, recovery tools, and procedures to ensure they are ready and functional when needed. As a minimum, MSP/MSSP clients should prepare:
Backup solutions: Implement a comprehensive backup strategy, including:
- Cloud backups (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage) for offsite data protection.
- On-premises backups for local redundancy.
- Adherence to the 3-2-1 backup rule (3 copies of data, 2 different media, 1 offsite).
Disaster recovery planning: Develop a detailed disaster recovery plan with clear:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum acceptable time to restore systems after an outage.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum acceptable amount of data loss in case of an incident.
- Business continuity planning to ensure critical operations continue during disruptions.
6. Conduct Employee Cyber Training
The human factor is often the weak spot of many cybersecurity strategies. Therefore, it’s no surprise that insurers prefer policyholders who consistently invest in effective employee training and education on cyber threats that involve social engineering techniques, like:
- Phishing and social engineering awareness
- Password security best practices
- Safe web browsing habits
- Data security policies and procedures
- Recognizing and reporting suspicious activity
MSP/MSSP clients can utilize a learning management system (LMS) to deliver and track training. Another best practice is to adapt training to the knowledge levels of each person/department/role; after all, organizations can’t expect a marketing professional to have the same in-depth understanding of cybersecurity as a developer.
7. Execute Regular Vulnerability Scans
Cyber threats and risks can morph and change, both due to external factors and internal ones (such as introducing new connected systems to the organization’s network). Insurers expect businesses to stay ahead of the curve by providing records of regular:
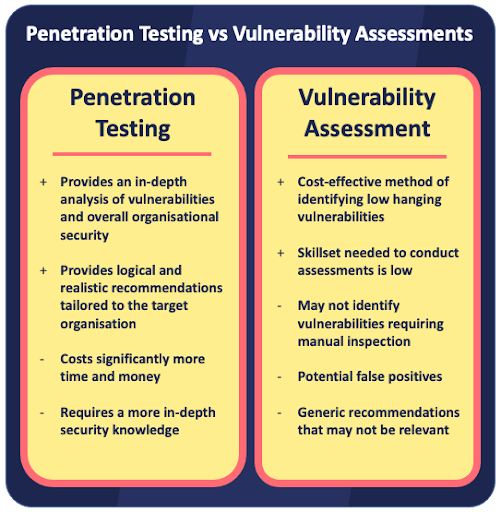
- Vulnerability scans: Regularly scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration tests: Conduct periodic penetration tests to simulate real-world attacks and identify vulnerabilities that automated scans might miss.
- Third-party risk assessments: Assess the security posture of third-party vendors and partners who have access to your systems or data.
8. Keep All Data Assets Classified and Handled Accordingly
Data asset classification goes hand in hand with IAM and access control enforcement. By segmenting data according to sensitivity and value, the organization can effectively focus protection efforts on the most valuable assets at risk.
Insurers favor organizations with a clear data classification policy to identify sensitive data (such as client payment information or patient health records) and intellectual property on business servers and systems. In addition, the insurer will expect to see a data encryption policy that protects this data from unauthorized access, even if the database is compromised.
9. Schedule Regular Software Updates and Patches
Regular application of security patches and software updates are key to protecting systems from known vulnerabilities—a positive effort in the eyes of insurers, and an essential addition to any cyber insurance risk assessment. The easiest way to achieve this is by automating patching and updating policies:
- Patch management: Implement a patch management system to automate the deployment of software updates and security patches.
- Vulnerability prioritization: Prioritize patching based on the severity of vulnerabilities and the likelihood of exploitation.
- Rollback plans: Develop rollback plans in case patches cause unexpected issues.
Preparing Organizations for a Cyber Insurance Risk Assessment with Cynomi
In 2025, insurance providers will demand that businesses showcase their commitment to cyber risk management. As part of the underwriting process, they will often conduct a cyber risk insurance assessment to determine the level of said commitment and demand assurances and proof for every item on their cyber insurance application form.
Cynomi’s AI-driven platform enables customized risk assessment scenarios that help MSPs/MSSPs prepare their clients for insurer scrutiny. Cynomi features automated policy creation and management features, plus actionable remediation plans, helping MSPs/MSSPs continually improve their clients’ cyber resilience and maintain insurability.
Cynomi’s vCISO platform automates cyber assessment processes, making them easy and efficient. Its client-facing dashboards and reporting features allow MSPs/MSSPs to prove ongoing success, show cybersecurity posture, and highlight upsell opportunities to close security gaps. Whether your MSP/MSSP strives to scale or set up vCISO services, the Cynomi platform makes these goals achievable while reducing operational costs and professional knowledge gaps.
Book a personal Cynomi demo today.