
You can be over-prepared for many things, like packing an overflowing suitcase for a two-night trip. Yet there’s one thing that you can never be too ready for: Cyber threats.
In fact, most organizations are woefully unprepared to deal with the realities of cyber attacks, with even dedicated security teams averaging 277 days to identify and contain a data breach. When budgets are tight, and your resources are spread across diverse clients, cyber risk management can help you deliver prioritized and tailored cybersecurity strategies for your clients when they need it most.
What is cyber risk management?
Cyber risk is the likelihood of an attack, and cyber risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats as a preventative measure before they can damage your clients’ organizations. Every connected system is exposed to cybersecurity threats, and you cannot eliminate risk for your clients – you can only manage it.
Why You Need Cyber Risk Management
Cyber risk management is a fundamental tool for investing in protecting digital assets with the greatest potential to be compromised. By doing so, you also prevent the most damage with the least amount of resources. From this perspective, cyber risk management is extremely beneficial in helping MSP/MSSPs with prioritization. You can identify and focus your efforts on the threats with the highest risk and make data-driven decisions on what action to take and when.
With compliance standards in mind, cyber risk management can help ensure the correct measures are taken to reduce potential legal ramifications. Constant monitoring and reporting (two key components of cyber risk management) help provide the necessary documentation to remain compliant.
4 Popular Cyber Risk Management Frameworks
Cyber risk management frameworks are government or organization standards that help guide risk management plans. Let’s review some of the most popular frameworks.
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this option provides a structured approach comprised of five core functions:
- Identify: Review your client’s systems, assets, data, and capabilities.
- Protect: Implement safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical services.
- Detect: Develop and implement activities to identify cybersecurity events.
- Respond: Create action plans in the event of cybersecurity incidents.
- Recover: Design continuous monitoring and maintenance plans for resilience and restore capabilities or services impaired due to a cybersecurity event.

2. ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for information security management systems. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability by safeguarding sensitive information through a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) approach. The PDCA cycle is a continuous improvement model that requires regular review and improvement of information security management to ensure its effectiveness and relevance to emerging threats.
3. CIS Controls
Developed by leading experts, the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls focuses on actionable security practices proven to mitigate the most prevalent cyber threats. The controls support and promote the need for risk management and dynamic risk assessments.
Based on their effectiveness and ease of implementation, the controls are organized into three Implementation Groups (IGs):
- Essential Cyber Hygiene (IG1): Every organization should implement Basic cyber hygiene practices to defend against the most common and pervasive attacks. Examples include controlling hardware assets and web browser protections.
- Fundamental Controls (IG2): Building upon IG1, IG2 adds more advanced security measures to address more sophisticated attacks and protect sensitive data. Examples include malware defenses and penetration testing.
- Organizational Controls (IG3): Implementing advanced security measures to protect against the most sophisticated attacks and ensure the highest cybersecurity maturity level. Examples include security awareness training and secure software development practices.
4. PCI DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) aims to protect cardholder data from theft, fraud, and unauthorized access. PCI DSS compliance is mandatory for any organization that stores, processes or transmits credit card information.
7 Essential Components for Cyber Risk Management
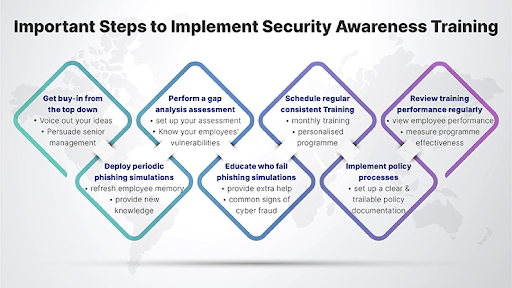
1. Security Awareness Training Program
Your clients’ employees are often the weakest link in any cybersecurity strategy. Security awareness training helps prevent employees from falling victim to scams like phishing attacks and promotes a security-aware culture.
Developing and recommending engaging and interactive training materials tailored to specific roles and responsibilities helps ensure nobody is overwhelmed with unnecessary complexity. Training sessions should be conducted regularly at set intervals to keep employees up to date on recent cybersecurity threats.
Remember to test the employees regularly using social engineering tactics. Otherwise, you’ll never know how they’d perform in a real-life scenario.
2. Vendor Risk Management Policies
Any vulnerability in a third-party vendor carries over into your clients’ systems. Vendor risk management policies communicate guidelines and procedures for evaluating third-party services to avoid unnecessary cybersecurity risks.
Develop and maintain a security checklist to investigate potential vendors for vulnerabilities before acquisition. When your clients partner with vendors, ensure they adhere to the same regulatory standards the client is bound by. Any signed contracts should include security requirements the vendor must uphold to maintain the relationship.
3. Risk Prioritization and Assessment
Without prioritizing risk, you can’t manage it. Risk prioritization and assessment are essential to risk management and the best way to prevent wasted resources. A simple formula of severity score multiplied by likelihood will provide an overview of critical security issues.
To get the most out of the process, your MSP/MSSP can complete an inventory of the client’s digital assets, attack vectors, and potential damage in case of a breach. Risk assessment frameworks or methodologies, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27005, can help guide the risk prioritization process. Use a risk assessment template to help prioritize vulnerabilities and remediate them so you can assign resources appropriately.
Yet, conducting a risk assessment can be a time-consuming and expensive challenge for InfoSec teams and the MSPs guiding them – especially if you have limited resources to dedicate to the process.
The alternative option is automating scale risk assessments with a third-party platform. For example, if you opted for a platform like Cynomi, you could benefit from automated risk scoring based on each client’s unique security profile. The ability to scale is coupled with highly customized assessments that fit each organization, and each client’s security posture and risk areas are calculated based on relevant factors like company size and available assets.
4. Network Security Audits
Proactively address vulnerabilities and weaknesses in network security by performing routine audits of controls and configurations. Anything connected to the internet is a potential weak point, but physical access to a part of a local network may grant unauthorized access to sensitive parts of the network.
Manually auditing networks is an arduous task that wastes resources, so many MSPs turn to automated scanning tools to evaluate configurations. Documenting audit findings and keeping network logs is also essential, especially if you must submit documentation for clients’ compliance purposes.
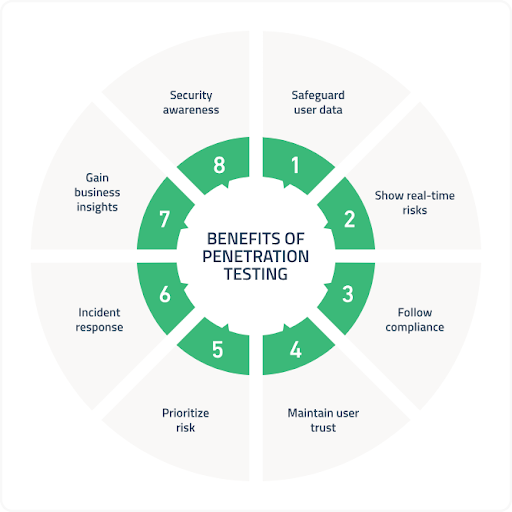
5. Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, involves simulating cyber attacks to identify vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and applications. You can perform penetration testing using various automated tools such as ZAP or Wireshark as part of your MSP software toolkit or guide your clients through the process.
Other tips include:
- Always define the penetration testing scope based on risk to prevent wasted resources.
- Document target systems, testing methods, and rules of engagement before embarking on this voyage.
- Penetration testing is ongoing as systems and requirements change over time, so perform them regularly.
6. Data Management
Data management involves implementing policies and procedures for the secure handling, storage, and disposal of sensitive data throughout its lifecycle. Some compliance standards, such as GDPR, require you to guide your clients in setting up processes for managing requests for personal data review or disposal. Best practices include:
- Classify data based on sensitivity and regulatory requirements, such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property.
- Ensure data is appropriately encrypted both in rest and transit.
- Adhere to the principle of least privilege when defining access policies to reduce risks of unauthorized access and leaks.
7. Incident Response Plan
Cybersecurity is about risk management, not elimination, so all MSP/MSSPs must have a plan to respond to incidents. A good response plan will minimize the impact on your client’s operations, reputation, and finances in the unfortunate event of a breach.
Establish clear roles and responsibilities and predefined procedures based on scenarios you establish that are most likely to occur. Tabletop exercises and simulations are good best practices for testing the effectiveness of your response plan. Above all, communication is vital when executing a response plan, so establish clear communication channels to notify stakeholders, clients, employees, partners, compliance authorities, and law enforcement when an incident occurs.
Cater to Every Client’s Risk Status with Cynomi
Cyber risk management aims to remain vigilant against evolving threats by helping your team keep their eye on the ball. Keeping up with risk assessments for your client base is a tough task, requiring time and financial investment, plus the expertise of your existing team.
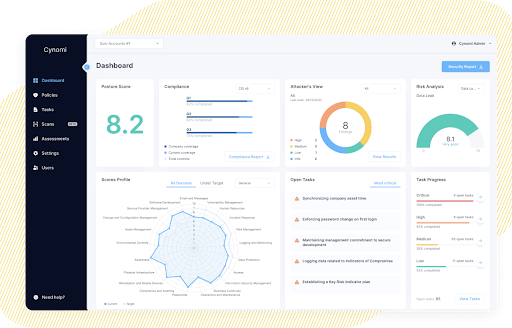
Cynomi’s AI-powered, automated vCISO platform offers MSP/MSSPs everything you need to assess, plan, remediate, manage, measure, optimize, and report for your clients. Cynomi provides continuous real-time assessments of security posture, risk levels, and compliance readiness so you can do your job more effectively and efficiently.
Unlike one-time risk assessments that generate snapshots of the client’s security posture and risk, Cynomi continuously and in real-time assesses your client’s security posture, risk level, and compliance readiness. Cynomi updates the policies, remediation plan, and task criticality based on updates and changes in the client environment, industry standards, and threat landscape so you can guide them in staying one step ahead of threats.
Schedule a demo today to discover how you can leverage Cynomi to streamline operations and offer your clients effective risk management services.