7 Risk Assessment Methods to Streamline Risk Management

Cybersecurity is all about the fear of the unknown. In reality, you never truly know what damage or consequences an attack could cause your clients’ organization. But as their MSP of choice, it’s your job to predict the unpredictable.
Cybercrime will reach $23 trillion by 2027 – that’s a lot of threats, bad actors, and risk pummelling your clients’ businesses from all angles. Conducting a risk assessment is one way to gain visibility over prolific threats and mitigate them before they occur. While there are various risk assessment methods you can use, the challenge lies in identifying which one is best for you and your clients.
What are risk assessment methods?
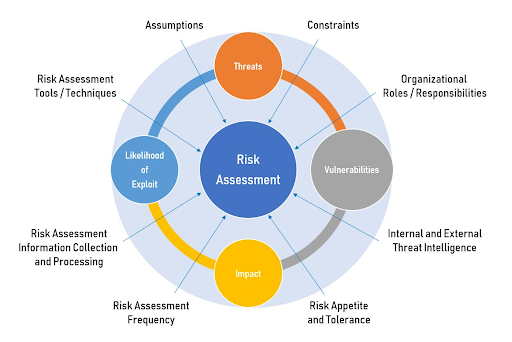
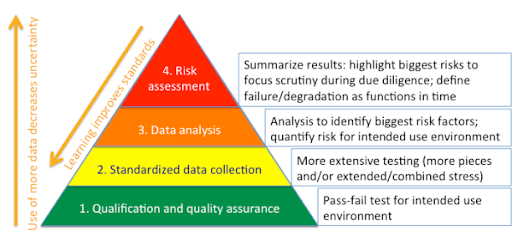
A risk assessment is a systematic process for identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise sensitive data or disrupt business operations. Whether your clients are large enterprises or startups, their data is a target, including customer information, financial records, or proprietary information.
Risk assessment methods provide a comprehensive understanding of your clients’ cybersecurity risk profile. It includes identifying the threats they are most vulnerable to, their potential impact, and the likelihood of them occurring. With this information, your MSP/MSSP can make informed decisions about allocating resources and implementing security measures tailored to their needs. It’s about being proactive, not reactive.

Why do you need risk assessment methods?
1. Proactive Threat Identification and Mitigation
Risk assessments enable you to proactively identify and prioritize vulnerabilities in your clients’ systems, networks, and applications before malicious actors exploit them. It includes identifying potential attack entry points, weaknesses in security configurations, and inadequate access controls. Addressing these vulnerabilities can significantly reduce the risk of a successful cyber attack.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with cybersecurity standards such as ISO 27001, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, or HIPAA is mandatory in many industries. Risk assessments are an essential part of demonstrating compliance with these standards. They provide evidence that you and your clients are committed to protecting sensitive data and meeting regulatory requirements.
3. Data-Driven Security Investments
Risk assessments offer a quantitative and qualitative analysis of potential risks, allowing you to decide where to invest cybersecurity budget. By understanding the potential financial impact of different threats, you can prioritize security measures that offer the greatest return on investment.
4. Incident Response Preparedness
A well-conducted risk assessment identifies potential scenarios that could lead to security incidents. This information is crucial for developing effective incident response plans. Knowing what to expect can prepare your team to respond quickly and effectively to minimize damage and downtime.
5. Continuous Security Improvement
Cybersecurity is more than just a one-and-done task. Regular risk assessments provide a feedback loop that allows you to identify emerging risks, evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures, and make necessary adjustments to maintain your clients’ security posture. Also, risk assessments may help you decide what to add to your suite of MSP software solutions based on the current cybersecurity landscape.
4 Ways to Choose the Right Risk Assessment Methods
1. Scope and Depth
The scope of your assessment should align with your clients’ specific needs and risk profile. Consider factors like the organization’s size, the IT infrastructure’s complexity, and the data’s sensitivity. For example, a smaller organization with limited resources opts for a less comprehensive assessment, while a larger organization with critical assets requires a more in-depth analysis.
2. Quantitative vs. Qualitative
Quantitative risk assessments focus on assigning numerical values to risks, such as financial impact and probability of occurrence. It allows for a more objective evaluation of risks and prioritization of mitigation efforts. On the other hand, qualitative assessments rely on expert judgment and qualitative descriptions to assess the impact and likelihood of risks. The choice between these approaches depends on data availability, the precision required, and the organization’s risk culture.
3. Industry Standards and Regulatory Requirements
If your organization operates in a regulated industry, you must ensure that your risk assessment methods comply with relevant standards and regulations. For example, healthcare organizations must adhere to HIPAA, while financial institutions must comply with GLBA.
4. Resources and Expertise
The complexity of the chosen risk assessment method should align with the available resources and expertise within your organization. Some methods require specialized knowledge and tools, while others are more accessible to general IT staff. It’s essential to balance the rigor of the assessment and the resources required to conduct it effectively.
For some MSP/MSSPs, choosing a risk assessment method is only the first challenge. Internal knowledge gaps, headcount shortages, and budget also contribute to the complexity of conducting a risk assessment for your clients. In this instance, many organizations turn to automated solutions like vCISO platforms to help deliver risk assessment services efficiently with the resources you currently have.
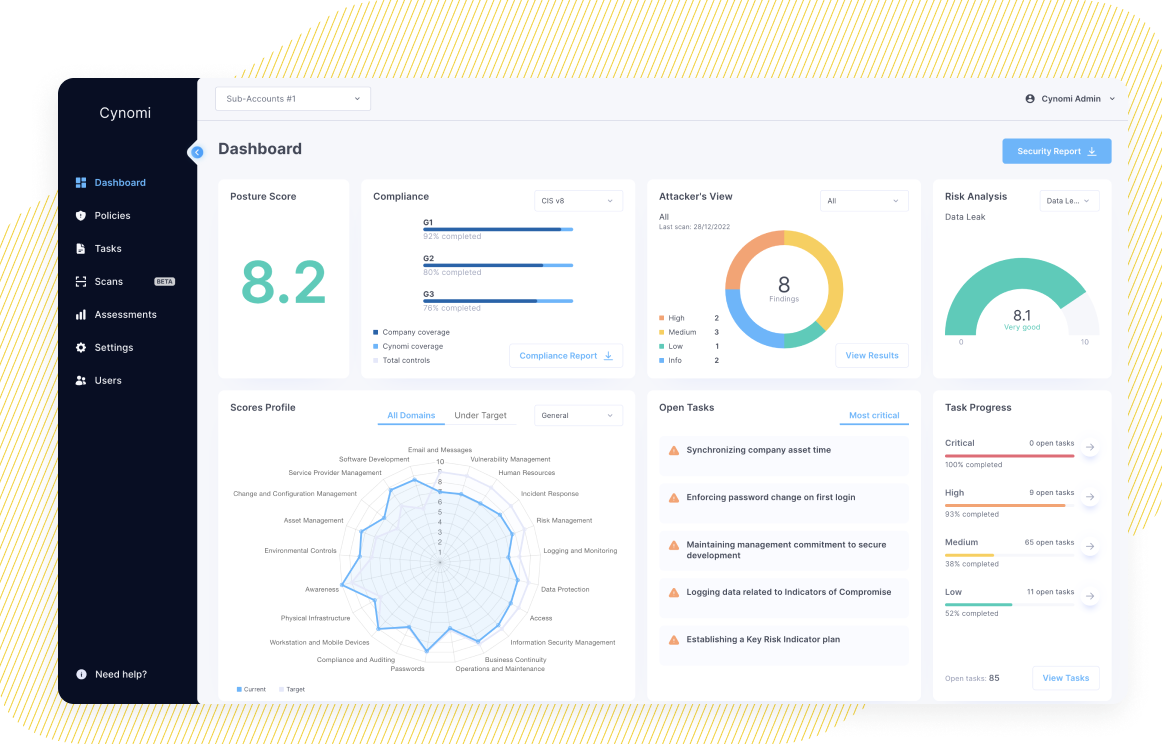
For example, Cynomi enables you to provide comprehensive risk assessments to each client, including automatically generated tailored policies and strategic remediation plans with prioritized tasks. Therefore, assessment capabilities should be on every vCISO checklist.
7 Risk Assessment Methods to Streamline Risk Management
1. Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)
QRA is a mathematically rigorous approach that assigns numerical values to risks. It involves calculating the Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE), which is the product of the Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) and the Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO). SLE is the estimated financial loss from a single event, while ARO is the frequency of expected events occurring in a year.
The results of QRA are often expressed in monetary terms, making it easier for end-clients and stakeholders to understand the financial implications of different risks. For example, a QRA might estimate that a data breach could cost a company $500,000 annually, while a ransomware attack could cost $250,000. Hence, the business can use the information to prioritize security investments and allocate resources accordingly.
2. Qualitative Risk Assessment (QLRA)
QLRA is a subjective assessment that relies on expert judgment to categorize risks based on their likelihood and impact. This method uses descriptive scales, such as low, medium, and high, to rate risks. While QLRA needs more precision of QRA, it can be valuable when quantitative data is not available or reliable.
It’s also helpful in assessing new or emerging risks where historical data may not exist. For example, a QLRA might assess the risk of a new type of malware as ‘high’ due to its potential to exploit a critical vulnerability in a widely used software application.
3. Asset-Based Risk Assessment (ABRA)
ABRA focuses on identifying and evaluating risks to specific assets within an organization. This method involves categorizing assets based on their value (e.g., critical, high, medium, low), identifying potential threats to each asset, and estimating the impact of a loss or compromise.
Asset-based risks can help you prioritize security measures for your most valuable assets. For example, a company might implement more stringent access and cis cyber controls for its customer database than its marketing materials.
4. Vulnerability-Based Risk Assessment (VBRA)
Vulnerability assessments involve scanning systems, networks, and applications for vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. It uses automated tools that identify known vulnerabilities based on Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) databases.
Once identified, vulnerabilities are assessed based on their severity and potential impact. VBRA is an essential component of any vulnerability management program and helps to ensure that security patches are applied promptly to mitigate risks.
5. Threat-Based Risk Assessment (TBRA)
TBRA identifies and assesses specific threats to your clients’ organizations, such as malware, phishing attacks, or insider threats. It involves analyzing threat intelligence data from various sources, including security vendors, government agencies, and open-source intelligence.
TBRA helps you understand the current threat landscape and tailor security measures to mitigate the most relevant threats. For example, suppose a TBRA identifies a surge in phishing attacks targeting a client’s industry. In that case, you might recommend additional email filtering and employee training to reduce the risk of a successful attack.
6. Dynamic Risk Assessment (DRA)
DRA recognizes that risks are not static and can change rapidly due to new vulnerabilities, emerging threats, or changes in the business environment. This method involves continuous monitoring of the threat landscape and adjusting risk assessments in real time based on new information.
Dynamic risk assessments can help you adapt security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats. For example, suppose a new zero-day vulnerability is discovered in a widely used software component. In that case, a DRA can trigger an immediate assessment and response to mitigate the risk.
7. Site-Specific Risk Assessment (SSRA)
SSRA focuses on the risks associated with a specific physical location or facility. These risks include natural disasters, physical security breaches, and environmental hazards. SSRA is essential for organizations with multiple locations, as the risks can vary significantly from one site to another.
For example, a location in a flood zone might require different data center security measures than one in a seismically active region.
Automate Risk Assessment Processes with Cynomi
Cynomi’s AI-powered vCISO platform empowers MSPs and MSSPs to navigate these treacherous waters. With built-in automated smart and adaptive questionnaires, Cynomi makes the risk assessment process quicker and simpler. Our platform also enables you to deliver comprehensive risk assessments to each of your clients, including automatically generated policies and strategic remediation plans with prioritized tasks.
Built-in self-guided and automated discovery questionnaires help MSPs/MSSPs gain visibility over end-clients’ cybersecurity posture. Cynomi supports the risk assessment/audit process with scans to uncover critical vulnerabilities in externally visible IPs and URLs, including ports, protocols, encryption, websites, and more.
Discover how Cynomi can transform and automate your risk assessment processes by booking a demo today.

Keeping you safe 24/7
Meet Cynomi Team Learn More