
Companies are beginning to scramble to meet the demands of the NIS2 Directive, which came into force on October 17, 2024. When the overwhelming spreadsheets and complexity of the compliance requirements become too much, organizations often turn to MSPs and MSSPs for a helping hand. Then, MSPs/MSSPs are pulled into the world of policies, assessments, and mapping controls—a space that demands expertise but eats away at your resources.
For managed security providers, the challenge is clear: how do you deliver the compliance guidance your clients need without exhausting your team or sacrificing efficiency? With cybercrime set to reach $10.5 trillion in 2025, the time to act towards NIS 2 compliance is now.
The NIS 2 Directive in a nutshell: What does it mean for your clients?
The NIS 2 Directive (Network and Information Security Directive 2) is the European Union’s latest framework aiming to uniformly bolster cybersecurity across EU member states. Building on its predecessor, NIS1, this updated directive expands its reach to include more sectors and businesses. The expanded regulation reflects the growing interdependence of digital and physical infrastructure across sectors and economies.
Its purpose isn’t to burden businesses but to create a collective baseline for managing cybersecurity risks to develop a stronger, more resilient digital ecosystem across Europe. Clients will likely evaluate MSPs/MSSPs on their ability to guide them in implementing technical and organizational controls, such as vulnerability assessments and supply chain security, to defend against evolving threats.
However, it’s not just about tools and processes; NIS 2 demands accountability at the leadership level by mandating that those in management positions actively oversee and understand their company’s cyber risks.
4 Example Requirements for the NIS 2 Directive
Within the wordy 73-page official NIS 2 document are ten key security requirements the EU refers to as cybersecurity risk management measures. These measures were derived from an “all-hazards approach that aims to protect network and information systems and the physical environment of those systems from incidents.” Here are four notable requirements all MSPs/MSSPs should know about.

1. Incident Handling
A requirement that got a lot of publicity in the NIS 2 directive is the need to notify authorities about significant cybersecurity incidents no later than 24 hours after detection. This initial notification is called an early warning; NIS 2 also mandates an incident notification without undue delay and within 72 hours of becoming aware of an incident.
This requirement emphasizes the need for real-time monitoring and well-rehearsed response procedures. While the short timeline might feel challenging, it can only be a good thing if better incident handling drives investment in streamlined reporting systems and incident response plans.
2. Supply Chain Security
The NIS 2 Directive introduces obligations to evaluate and secure third-party suppliers—this acknowledgment of supply chain security points to threat actors relentlessly targeting and exploiting supply chain vulnerabilities.
This requirement translates into closer scrutiny of vendor relationships, contract terms, and third-party risk assessments. Where third-party software is involved, MSPs/MSSPs and their clients must hone in on the supplier’s secure development practices.
3. Business Continuity
The business continuity requirement shows how the EU maintains essential services in vital sectors even during serious cyber incidents. MSPs/MSSPs and their clients will need to do more than ever to invest in resilient systems that prioritize continuity. This requirement may involve integrating automated backup solutions, advanced disaster recovery tools, and incident simulation exercises. Beyond the technical aspects, organizations must focus on creating a culture of preparedness and ensuring all staff understand their roles during a crisis.
4. Secure Authentication
The NIS 2 Directive calls for secure authentication through multi-factor authentication (MFA) or continuous authentication. The difference between the two lies in their approach to verifying identity:
- MFA relies on a one-time verification process that uses at least two factors: something the user knows (like a password), something they have (like a smartphone or token), or something they inherently are (like a fingerprint or facial recognition). Once verified, the user gains access until the session ends or they log out.
- Continuous authentication goes beyond a one-time check. It continuously verifies the user’s identity throughout the session by monitoring behavioral patterns (like typing speed or mouse movements) or contextual data (like location or device). If anomalies are detected, access can be restricted or revoked in real time.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the NIS 2 Directive?
The NIS 2 Directive establishes a two-tier financial penalty system, distinguishing between “essential” and “important” entities. For essential entities, the Directive sets a maximum fine of at least €10 million or 2% of the organization’s total worldwide annual turnover, whichever is higher. For important entities, the maximum fine is at least €7 million or 1.4% of the total worldwide annual turnover, whichever is higher.
The shift to management accountability compels your clients’ board members and other senior management staff to understand the strategic implications of cybersecurity. The EU wants to instigate a cultural change where cybersecurity becomes a boardroom issue that fosters better decision-making and resource allocation.
In practical terms, the EU imposes punitive measures for individual board members who fall short of their responsibilities; potential sanctions include public statements naming responsible individuals and revoking the right to hold management positions where there are repeated violations of the Directive.
It’s also worth noting that while the Directive provides baseline figures for company fines, the supervisory authorities in individual EU Member States have the authority to set higher penalties within their national legislation. In addition, the Directive empowers national authorities to impose non-financial penalties, such as orders to comply, mandatory instructions, and security audits.
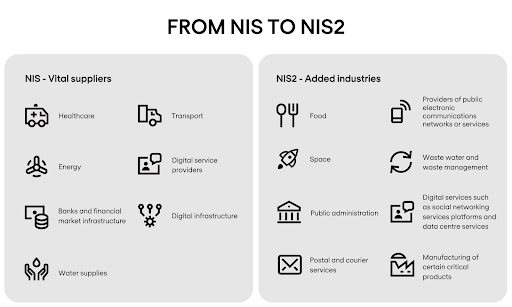
NIS 1 vs NIS 2 Directive: Key Differences
The original NIS interaction was criticized for its vague requirements and inconsistent implementation across EU member states. The table below shows some ways in which the NIS 2 Directive addresses the shortcomings of its predecessor.
| Aspect | NIS1 | NIS 2 | Improvement in NIS 2 |
| Scope | Limited to a narrower set of “essential services” in six sectors. | Expands to include far more sectors (e.g., public administration, waste management, food production). | Broader coverage ensures more sectors are safeguarded, which better reflects the nefarious and widespread threat landscape. |
| Enforcement Consistency | Variability in implementation across EU member states. | Harmonized minimum requirements across all member states. | Reduces fragmentation and creates a more uniform level of cybersecurity across the EU. |
| Incident Reporting | Required but lacked specificity in timelines and thresholds. | Mandatory reporting within 24 hours for significant incidents. | Clear timelines improve response coordination and reduce the spread of cyber incidents. |
| Board-Level Accountability | Not explicitly required. | Requires executive boards to oversee cybersecurity risks. | Embeds cybersecurity as a business priority. |
| Supply Chain Security | Little to no mention. | Explicit focus on assessing and securing supply chain risks. | Recognizes and mitigates the growing threat of supply chain attacks. |
| Penalties | Vague and inconsistent penalties. | Tiered fines up to €10 million or 2% of turnover, with individual liability for negligence. | Creates stronger deterrence and incentivizes compliance at both organizational and individual levels. |

Does your client’s business need to comply with the NIS 2 directive?
The answer to this question can become convoluted when you start to delve into whether your clients are an important or essential entity for compliance purposes. However, the simple yes or no answer is to first figure out if the client operates in any of the 11 sectors of high criticality or any of the seven critical sectors. SMEs (50-249 employees or over 10 million in revenue) and larger companies must comply with the NIS 2 Directive if they operate in any of these 18 sectors.
Small and micro-enterprises of fewer than 50 employees are generally exempt unless they are in specific sub-sectors of the highly critical sectors of Digital Infrastructure and Public Administration Entities.
Another interesting aspect of the NIS 2 Directive is that it retains the EU’s general trend of extraterritoriality in its regulations (like GDPR). This rule means compliance is also necessary if the client is an essential or important entity providing services or carrying out activities in the EU.
Transforming Compliance Assessments into a Competitive Advantage
NIS 2 is officially in force, and the stakes for non-compliance are high. More companies will continue to turn to MSPs and MSSPs for guidance in navigating its complex requirements. Tools and platforms that automate the manual work can potentially transform compliance assessments aligning with frameworks like NIS 2 from a time-consuming challenge into a value-added service that you provide with efficiency.
The manual effort required—auditing frameworks, creating tailored policies, and identifying gaps—can strain your team and divert focus from other high-value services you offer. With Cynomi, you can streamline these assessments and deliver exceptional NIS 2 compliance support to clients while freeing up resources to continuously grow your business. Moreover, showing the gaps to compliance through a third party like Cynomi, helps you explain the need of other cybersecurity services and solutions to your clients, making upsell more easy.
Cynomi simplifies your compliance offerings through a vCISO platform that automatically matches each client’s cyber profile with standards, frameworks, and regulations like NIS 2. Automated scans can uncover critical vulnerabilities in externally visible IPs and URLs, including ports, protocols, encryption, websites, etc., to help determine clients’ areas of non-compliance with NIS 2’s technical controls.
Request your demo here.