The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) provides organizations with a structured approach to managing cybersecurity and data privacy risks. By integrating security, privacy, and risk management into a single, repeatable framework, it ensures that organizations can continuously evaluate and strengthen their security posture.
Widely adopted by U.S. federal agencies, contractors, and private organizations, the NIST RMF plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data, meeting compliance requirements, and proactively mitigating threats. Its comprehensive approach makes it a trusted standard across public and private sectors alike.
What Is the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)?
The NIST Risk Management Framework is a systematic, repeatable process for identifying, assessing, and managing cybersecurity risks. Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the RMF integrates key principles of security and privacy into risk management activities, ensuring continuous improvement over time.
The primary purpose of the RMF is to provide organizations with a consistent and structured way to handle cybersecurity risks. It aligns closely with compliance requirements for federal agencies and contractors while offering value to private businesses seeking to implement best-in-class risk management practices.
Whether required for federal operations or adopted voluntarily, the RMF enables organizations to balance security with operational needs, ensuring both protection and efficiency.
Why Is the NIST RMF Essential for Organizations?
The NIST RMF provides organizations with a robust framework for navigating today’s dynamic cybersecurity landscape. Its comprehensive approach ensures that risks are managed throughout the entire lifecycle of systems and data.
Adopting the RMF offers several key advantages:
- Comprehensive Risk Management: Encompasses everything from initial risk assessment to continuous monitoring, ensuring no phase is overlooked.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: Aligns with regulatory standards such as FedRAMP, HIPAA, and CMMC, simplifying audits and certifications.
- Proactive Threat Mitigation: Enables early detection and mitigation of threats, reducing the potential impact of cybersecurity incidents.
- Operational Resilience: Supports business continuity through informed, risk-based decision-making.
- Global Recognition: Established as a trusted framework for public and private sectors worldwide.
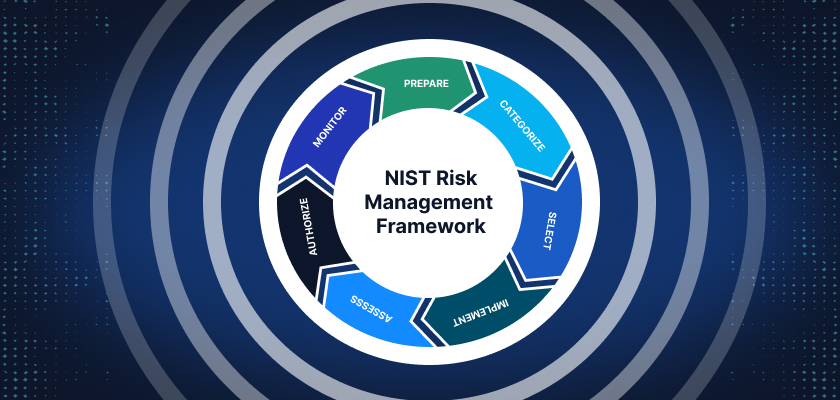
The NIST RMF Process: Key Steps Explained
The NIST RMF breaks down risk management into seven distinct steps, ensuring a thorough and systematic approach:
| Step | Objective | Actions |
| Prepare (Step 0) | Establish the risk management process, define roles, and set security expectations. | Identify key stakeholders, define business needs, and outline risk tolerance. |
| Categorize Information Systems (Step 1) | Determine the system’s sensitivity, criticality, and impact level. | Use data classification methods based on confidentiality, integrity, and availability. |
| Select Security Controls (Step 2) | Choose baseline security controls based on system categorization. | Reference NIST SP 800-53 to select relevant controls and tailor them as needed. |
| Implement Security Controls (Step 3) | Deploy selected controls across the system environment. | Follow implementation guidelines, perform initial testing, and document processes. |
| Assess Security Controls (Step 4) | Evaluate the effectiveness of implemented controls. | Conduct security assessments, vulnerability scans, and penetration testing. |
| Authorize the System (Step 5) | Obtain formal approval for system operation based on risk tolerance. | Submit findings for risk review, and secure authorization from leadership. |
| Monitor Security Controls (Step 6) | Continuously monitor system performance and compliance. | Use automated tools for monitoring, incident detection, and compliance reporting. |
Review NIST Controls: Implementation Guide & Best Practices for more information.
How the NIST RMF Works in Practice
The NIST RMF integrates risk management principles into daily operations to ensure a proactive approach to cybersecurity. By following the RMF steps, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, implement effective controls, and adapt to evolving threats.
Key elements of the RMF in practice include:
- Risk Identification: Recognizing potential threats, vulnerabilities, and risks within the organization’s IT environment.
- Risk Assessment: Conducting detailed assessments to understand the impact and likelihood of each risk.
- Risk Mitigation: Applying controls to reduce or eliminate identified risks and documenting mitigation strategies.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously evaluating system performance using automated tools and manual assessments to ensure ongoing compliance and improvement.
Key Benefits of the NIST RMF
Implementing the NIST RMF provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks while enhancing operational efficiency.
- Standardized Risk Management Process: Ensures consistency and reliability in managing risks across the organization.
- Enhanced Compliance Readiness: Simplifies adherence to regulatory frameworks like FedRAMP, CMMC, and HIPAA.
- Reduced Security Incidents: Proactively identifies and mitigates vulnerabilities to prevent data breaches and disruptions.
- Continuous System Monitoring: Offers real-time insights into security posture and system performance
- Decision-Making Support: Offers real-time insights into security posture and system performance
Manage Cybersecurity Risks with the NIST RMF
The NIST Risk Management Framework is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity, offering organizations a reliable and structured process for managing risks, ensuring compliance, and maintaining operational resilience. By adopting the RMF, businesses can strengthen their security posture and proactively address emerging threats while staying aligned with regulatory requirements.
Step-by-Step Guide to NIST Compliance for Service Providers
Simplify NIST compliance with a step-by-step roadmap, actionable best practices, and tools to help your MSP or MSSP scale services efficiently and securely.
Frequently Asked Questions About the NIST RMF
A structured process for managing cybersecurity and data privacy risks.
U.S. federal agencies, contractors, and private organizations seeking to adopt best practices.
Prepare, Categorize, Select, Implement, Assess, Authorize, and Monitor.
By providing a repeatable process to identify, mitigate, and monitor risks continuously.
<!– wp:cy/composite-cta {“name”:”cy/composite-cta”,”data”:{“field_67a48c39723da”:{“field_67a48c5b723db”:””,”field_67a48c6d723dc”:”Step-by-Step Guide to NIST Compliance for Service Providers”,”field_67a48c84723dd”:”Simplify NIST compliance with a step-by-step roadmap, actionable best practices, and tools to help your MSP or MSSP scale services efficiently and securely.”,”field_67a49410723e1″:”1″,”field_67a48c8d723de”:{“title”:”Download”,”url”:”https://cynomi.com/guide-to-nist-compliance-for-service-providers/”,”target”:”_blank”}}},”mode”:”edit”} /–>Mandatory for federal agencies and contractors; recommended for private organizations.